What is Decision Intelligence?
To better understand the concept of ‘Decision Intelligence’, first we need to outline what we mean by ‘Decision’. According to the Cambridge dictionary, “A decision is a choice that you make about something after thinking about several possibilities.”
When making decisions in both business and everyday life, we are usually driven by the current situation and environment, our knowledge of the issues, our past experiences, biases, emotions, desires, and intuitions. Often our decisions are also influenced by the stereotypes and misconceptions we hold and our own perceptions of the reality facing us.
This is typically how the human brain processes issues at hand and a combination of external and internal factors to make a choice. Very rarely does it consider all the influencing factors and perceives a holistic picture.
But that’s the human brain for you. When it comes to AI and decision-making, it’s a whole another ballgame. An AI system processes and analyzes huge data arrays in real-time, makes smart predictions based on the historical data, and suggests the best possible decisions based on available data sets and initially specified parameters.
In prescriptive analysis, it involves using data, algorithms, and computational methods to recommend specific actions or decisions based on data analysis and modeling. Prescriptive analytics goes beyond descriptive and predictive analytics, both of which are focused on understanding past events and predicting future outcomes. Instead, Prescriptive analytics aims to provide actionable insights that can be used to make informed decisions in real-time.
Broadly, there are two main differences between Human and AI decision-making:
- AI considers all the information available, while a humans consider limited data.
- AI is ultimately objective and neglects emotional factors.
Top 3 Trends Driving Adoption of Decision Intelligence
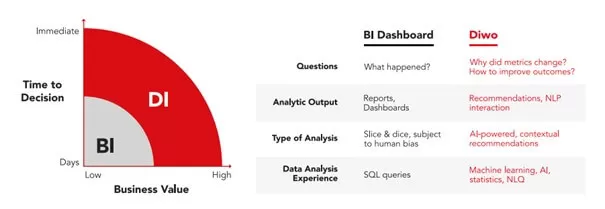
- In the past two decades, enterprises have made massive investments in BI and visualization tools, data lakes and machine learning platforms to deliver data-driven insights and optimize business outcomes. Despite the volume of insights being produced, effectively turning insights into action remains elusive to businesses. The final step in the analytics process in which insights are translated into outcomes that drive value – is still a challenge for many, if not most organizations.
- Digital transformation, global competitive dynamics and new expectations from customers require businesses to constantly look for faster ways to turn data into insights and recommendations into action. Business decision-makers need to go beyond descriptive BI reports and dashboards and leverage decision intelligence or DI, which provides deeper, more accurate insights and delivers data-driven, contextual recommendations at the point of decision.
- There will be 175 zettabytes of data worldwide by 2025, much of it unstructured. This massive volume of data won’t be processed manually. This is where organizations will need to use decision intelligence along with advanced machine learning algorithms. DI will augment human capabilities in the decision-making process with data and algorithms, thereby eliminating bias and enhancing the quality of decision-making. DI will also enable more responsive operations and ultimately, improved bottom-lines.
The Decline of Dashboards
BI reports and dashboards have been a mainstay of the analytics toolkit for the past 20 years. Dashboards are great for observing standard metrics from aggregated data at a high-level and with rigid, predetermined drill paths. But they cannot address follow-on questions such as “why” things are happening, or “how” you can affect change in performance. Although they can convey snapshots of important measures, dashboards struggle to offer context and nuance that effective data driven decision-making demands. Organizations today need an analytics platform that can do more than just visualize their data. A platform that facilitates decision-making and empowers business users to drive real-time decisions and action.
Moving from descriptive insight to recommendations for action requires knowledge of how the underlying data was generated, a deep understanding of the business context and critical thinking skills on part of the user to understand what the data does and does not mean. Dashboards don’t provide any of this; they provide the “what” but not the “why”. Even with predictive AI models, current BI tools have only offered possibilities, leaving human users unsure and unable to decide. Business users typically have no clear, logical step to take after they have viewed the data on their dashboards. They have seen a change in the data and ask, “now what?”
How Decision Intelligence Works
Decision Intelligence is a relatively new field which combines artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, contextual intelligence, NLP, and process automation techniques to help individuals and organizations explore, analyze, and make decisions based on data more effectively than they could manually with static reports and dashboards. Here are the key steps to understanding how decision intelligence works:
Define the decision problem
: The first step in decision intelligence is to define the problem that needs to be solved. This involves identifying the decision makers, the decision criteria, and the possible alternatives.Gather data
: Once the problem is defined, data is collected and organized. This may involve gathering data from internal sources such as databases, or external sources such as customer surveys or market research.Analyze data
: The data is then analyzed using various statistical and machine learning techniques to identify patterns, trends, and insights. This analysis helps decision makers better understand the problem and identify potential solutions.Develop models
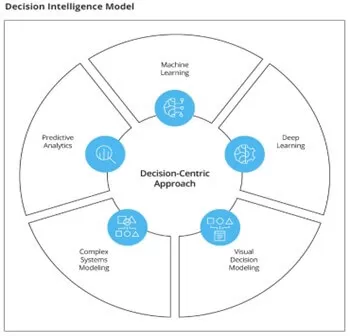
: Decision intelligence uses models to represent the decision problem and possible outcomes. These models can range from simple decision trees to more complex algorithms such as reinforcement learning or deep learning. Here is a whole set of technologies and algorithms that powers a decision machine:- Machine learning – ML algorithms work with a certain amount of structured data and make suggestions or decisions according to the specified parameters. Anti-fraud systems used by banks is the simplest example. For instance, when users access their banking app from the suspicious IP, the system decides on the necessity of additional user authentication.
- Deep learning – Deep learning is the next stage of machine learning evolution. In this case, a decision machine takes the previously made decisions and their outcomes into account when making each new suggestion.
- Visual decision modeling – AI decision-making serves as the reliable starting point, but the decisions are still made by the business owners and/or their employees. Visual decision modeling is one of the features of decision intelligence software to show the human decision-makers the available options and their outcomes.
- Complex systems modeling – One of the benefits of decision intelligence is to quickly build a complex business logic being guided by the available data and the final goal.
- Predictive analytics – The decisions AI systems make are based on quite accurate predictions. The simplest example is price prediction and automated optimization in retail. In this case, the suggestions made by decision intelligence are based on the current and historical price fluctuations, predicted demand, upcoming trends, and tons of customer behavior insights.
Test and refine models
: The models are then tested and validated using real-world data to ensure they accurately represent the decision problem and provide useful insights. This involves validating the models against historical data and making adjustments as necessary.Make decision
: The final step is to use the insights gained from the analysis and models to make an informed decision. The decision is made based on the best available data and the desired outcome.
The Benefits of Decision Intelligence for Business
Below are core benefits of decision intelligence solutions businesses can expect.
- Data-driven decisions: Despite the overwhelming evidence that data-driven decision-making can boost business growth, not all organization make optimal use of their data. To get a competitive advantage, you must correctly analyze the available data, make some predictions, and choose the best option. AI can take a better look at the data array and find invisible patterns and possible anomalies that can significantly influence the outcome.
- Faster decisions: According to a Gartner survey, 65% of decisions made lately are more sophisticated than earlier as they require more signoffs from multiple stakeholders involved. In other words, artificial intelligence decision making can deal with the fast-paced business realm as such systems are able to process huge amounts of data almost instantly.
- Multiple problem-solving options: AI-powered decision-making algorithms can also be quite flexible and highlight several outcomes of a certain decision when one of the parameters is changed. This feature can help the business to make the best choice from a multitude of options, considering their current goals and growth strategies.
- Mistakes and elimination of biases: There are at least nine types of cognitive biases (conservatism, base rate neglect, confirmation, sample size neglect, hindsight, anchoring and adjustment, mental accounting, availability, and framing) that can directly influence business decision outcomes. Decision intelligence allows avoiding them all since the correctly programmed algorithm takes an ultimately objective look at the available data.
The five pillars of Decision Intelligence maturity
The five pillars of Decision Intelligence maturity are a framework that organizations can use to assess and improve their decision-making processes. These pillars are based on the idea that decision-making is not just a one-time event but an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement. Here are the five pillars of Decision Intelligence maturity:
Data
: The first pillar is data, which refers to the quality and availability of data that is used to inform decision-making. To be effective, decision-making requires accurate and timely data that is relevant to the problem being addressed. Organizations that are mature in this pillar have robust data governance processes, including data quality control, data privacy and security, and data storage and retrieval.Analytics
: The second pillar is analytics, which refers to the methods and tools used to analyze data to derive insights and inform decision-making. Mature organizations have a range of analytics capabilities, including descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics. They also have a strong understanding of statistical concepts and can communicate insights effectively to stakeholders.Process
: The third pillar is process, which refers to the structured approach used to make decisions. Mature organizations have well-defined decision-making processes that are based on best practices and are aligned with their strategic goals. They also have clear roles and responsibilities for decision-making, and they document their decisions and the rationale behind them.People
: The fourth pillar is people, which refers to the skills and expertise required to make effective decisions. Mature organizations have a workforce that is trained in the principles of Decision Intelligence and has the necessary technical and soft skills to support effective decision-making. They also have a culture that values data-driven decision-making and encourages continuous learning and improvement.Culture
: The fifth pillar is culture, which refers to the values and beliefs that shape an organization’s decision-making processes. Mature organizations have a culture that values transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement. They also encourage experimentation and learning from failure, and they prioritize the use of data and analytics to inform decision-making.
The five pillars of Decision Intelligence maturity provide a framework for organizations to assess and improve their decision-making processes. By focusing on data, analytics, process, people, and culture, organizations can build a more effective and efficient decision-making process that supports their strategic goals. Decision Intelligence maturity is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement, but by investing in these five pillars, organizations can make better decisions that lead to better outcomes.
Conclusion
Decision intelligence is an important and growing field that is helping decision-makers make better decisions in today’s complex and fast-paced world. By leveraging the power of data and analytics, decision intelligence can help decision-makers make more informed decisions leading to better outcomes for individuals, organizations, and society. The methodology of decision intelligence involves a systematic and structured approach with the goal of using data and analytics to inform and improve decision-making. Decision intelligence has applications in a wide range of fields and can be particularly useful in situations where decisions are complex, involve uncertainty, and have significant consequences.











 Media Coverage
Media Coverage Press Release
Press Release
